-
Turn On Search Indexing Windows Vista
Turn Off Indexing in Windows for Better Performance. Turning off indexing on your hard drives is another very simple way to boost performance in your PC. Before I get into the details of turning off indexing, let’s try to go through the reasons why you would want to disable indexing in the first place and when you should leave it enabled. There are basically three cases as I see it when it comes to indexing, which makes it really easy to determine whether you should enable or disable indexing: 1. Really fast CPU (i. Slow CPU + any type of hard drive = don’t index.
Turn Off Indexing in Windows for Better Performance. Turning off indexing on your hard drives is another very simple way to boost performance in your PC. Before I get into the details of turning off indexing, let’s try to go through the reasons why you would want to disable indexing in the first place and when you should leave it enabled. There are basically three cases as I see it when it comes to indexing, which makes it really easy to determine whether you should enable or disable indexing: 1. Really fast CPU (i. Slow CPU + any type of hard drive = don’t index.
Family Search Indexing Windows 10
Enable or disable Instant Search. Turn on Instant Search. Select the Windows Search check box. Windows Vista or earlier Instant Search is enabled. Off Indexing Of Your Local Drive In Windows. Windows Vista, and Windows 7. Indexing is enabled because it helps Windows index your files and folder for faster. How to Disable Windows Search Indexing in Vista. Disable Vista Search Indexing, Disable Windows Search.
Windows 7 Turn Off Indexing
Search indexing service scans. Disable and Turn Off Windows 10 / 8.1 / 8 / 7 Search. 10 Ways and Secrets to Improve Windows Vista Performance; Fix Search Not. Published: May 4, 2009.
Any type of CPU + SSD hard drive = don’t index. So it basically comes down to the type of CPU and the type of hard drive. You never want to turn it on for an SSD drive and same goes if you have a slow CPU. Don’t worry, turning off the indexing service will do no harm to your computer. You may then ask, well how am I supposed to search for something!? Well, don’t worry, you can still search, it just won’t be indexed.
So ask yourself when was the last time you really searched for something anyway using Windows Explorer? I’ve haven’t performed a search in years now because I now rely mostly on cloud services or I just happen to be very organized and know where all my files are.
So now let’s get into how to actually disable indexing. Note: In order to not confuse, you should know that you can STILL search your computer in Windows 7 even with indexing turned off, it’ll just search without an index. I have found that at least in Windows 7, the search sucks whether or not you have indexing turned on or not. Turn Off Indexing Selectively. There are a couple of ways you can turn off indexing.
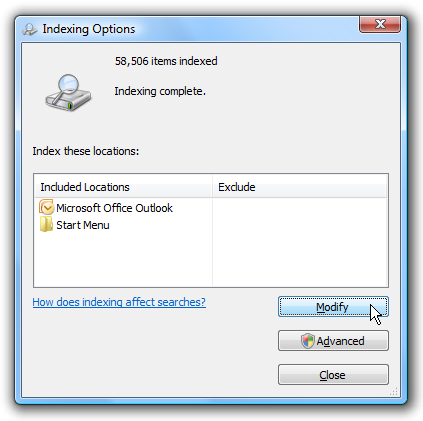
Firstly, if you still want to be able to search common locations like Documents or My Pictures, etc, then you can selectively disable indexing for other non- essential location. To do that, click on Start and type in indexing. The first option should be Indexing Options. Here you will see a list of the currently indexed locations.
You can click on the Modify button to change what locations you want indexed. By default, Windows 7 will index Outlook, IE history, any offline files, the Start Menu and your User directory, which contains Documents, My Pictures, etc. If you don’t need all the folders listed indexed, then go ahead and uncheck them after clicking on Modify. Since my My Pictures folder has over 5.
GB of photos all named DSCXXX or IMGXXX, there was no point in indexing that folder because I was never going to search it. All the photos in that folder were organized into subfolders by event, etc.
So when I disabled My Pictures indexing, I noticed a decent speed boost because Windows was no longer trying to index those files. In addition, I add hundreds of pictures a week to that folder, so the indexing never would stop. Remove Outlook from Indexing.
If you want to remove Microsoft Outlook from the search index, you may notice that it doesn’t appear in the top list, but does so in the bottom list. So how do you get rid of it from the search index?
To do that, you first have to open Microsoft Outlook and then click on File – Options. Now click on Search on the left side and click on the Indexing Options button on the right. It seems to bring up the same Indexing Options dialog, but now when you click Modify, you’ll be able to deselect Microsoft Outlook. Turn Off Indexing for a Drive. Another way to turn off indexing is to tell Windows not to index a particular drive.
I recently added a hard drive to my Windows 7 machine to use as a backup. By default, Windows was indexing files on the backup drive, which was useless since I was never going to search that drive. To turn off indexing on a drive, go ahead and open My Computer or Computer and right- click on your local drive (C, D, etc) and choose Properties. On the General tab, you’ll see a checkbox at the bottom called “Allow Indexing Service to index this disk for fast file searching” in Windows XP or “Allow files on this drive to have contents indexed in addition to file properties” in Windows 7 and 8. Go ahead and uncheck that and you’ll get a popup dialog box asking whether you want to apply these settings to all files and subfolders or just to the root of the drive: Choose all files and subfolders, otherwise it’s going to still index everything on the drive! Click OK and you’ll have to sit and wait for a few minutes as the settings are applied to all the files on your computer.
Unfortunately, every file in the file system has an attribute that tells Windows whether or not it should be indexed, so this has to to be updated for all files. If you get any Access Denied errors along the way, just go ahead and click Ignore All because it’s probably just system files that are currently in use.
In the example above, I chose the C drive, but you don’t have to turn indexing off for the C drive normally as the system and program files are not being indexed by default. If you have a secondary drive or other partitions, then it’s best to disable indexing using the method above. Completely Disable Indexing. There is one more way to disable indexing and it will totally turn it off. The above methods will reduce what’s indexed by Windows, but the indexing service will still be running. Here I’ll show you how to turn off the indexing service altogether, which is I’ve done and have never run into an issue where I needed it enabled. First open the Control Panel and click on Administrative Tools.
Then click on Services in the list. You can also open Services directly by typing services. Run dialog or Start Menu search box.
Now scroll down till you find either Indexing Service or Windows Search in the list of services. You’ll see it’s probably in the Started state and is set to Automatic. Double- click on Windows Search and click the Stop button to stop the service. Then change the Startup Type to Disabled. After this, you’re going to want to restart your computer. When you turn indexing off, you can still perform a search in Windows, it’ll just give you a message saying it’s going to be slower because there index is not running.
As I mentioned before, I did a test with the index on and off and performed a search on the entire C drive for a file in one of my indexed locations and the results were pretty much the same! It was literally only a few seconds difference, but both searches took over a minute. Probably the reason why I never use Windows search in the first place. If you have any questions about indexing in Windows, let us know in the comments.
Windows Indexing Features. Windows Search complies with the Windows Security model and is subject to frequent review. Microsoft Corporation has taken significant steps to help ensure the security of the index file. Windows Search runs as a system service; however, security trimming ensures users cannot access any data they do not have permission to see. Windows Search is designed to help ensure the security of the index files. Windows Search does not make the computer’s content accessible to Microsoft or anyone else.
The data structures of the index files do not lend themselves to easy reconstruction of a complete document. However, someone with enough tenacity and time could reconstruct the text for the majority of a document. This provides strong protection against offline attacks; online attacks are still possible by users with administrator access. Bit. Locker Drive Encryption provides enhanced protection against data theft by encrypting data operating system and data volumes. In Windows 7, Bit. Locker Drive Encryption works on removable drives.
We strongly recommend also Bit. Locking operating system volumes if you Bit.
Lock data volumes. While the Encrypting File System (EFS) can also be used, it is not recommended.
The Windows Search service runs under the Local. System account and needs access to the index files. As a result, EFS keys associated with the Local. System account must be used to encrypt the index files. Consequently, the index files are open to the following attacks. Online: Any administrative user can gain access to the encrypted index files by simply impersonating the Local. System account. Someone with physical access to the machine can use existing tools on the web to retrieve this key and access the encrypted index files.
Note. Users’ files are encrypted with EFS keys associated with individual users. These files do not have the risk detailed above as EFS keys are decrypted in a sequence that starts with a key derived from the user’s password. You cannot encrypt the index files with any user’s certificate other than Local.
System. For more information about the type of protection provided by both EFS and Bit. Locker, see the Security Analysis document in the Data Encryption Toolkit for Mobile PCs. For more information about Bit. Locker refer to Microsoft Tech. Net’s Windows Bit. Locker Drive Encryption Step- by- Step Guide. Utilizing Bit. Locker to protect the Index files.
Bit. Locker Drive Encryption provides enhanced protection against data theft by encrypting data operating system and data volumes. In Windows 7, Bit. Locker Drive Encryption works on removable drives. This section explores how Windows Explorer, the Library Management dialog, and the Windows Search indexer work with Bit. Locker- protected Drives.
For more information on how Bit. Locker works and how to configure it refer to the docs here: Drives on a system can have the following states with respect to Bit. Locker. Bit. Locker Off – Drive not encrypted for use with Bit. Locker. The drive is visible but its contents are not.
Windows Explorer: In Windows 7, the Windows Explorer displays the Bit. Locker state of the drives on a system in the Details pane. The right- click context menus for Bit. Locker offer the following goptions: Unlock Drive: selecting this option enables users to Unlock the Bit. Locker drive. Manage Bit. Locker: selecting this option brings up the Control Panel Applet to Configure Bit. Locker on drives on a system.
Libraries: In Windows 7, users can add both locked and unlocked Bit. Locker drives as library locations. Users can right- click drives in the Library Management dialog and select Unlock Bit.
Locked drives like they would do in Windows Explorer. Adding locations from already unlocked Bit. Locked drives is similar to adding locations from any other supported library location. Locking or unlocking Bit. Locker drives that are part of a Library location does not remove them from a library.
Users will have to manually remove these locations using the Library Management dialog. Search: Searching across Bit. Locked drives is similar to searching external drives or network locations. Search results from locked Bit.
Locker drives are not displayed when the drive is locked. The locked Bit. Locker drive is considered offline as its contents cannot be viewed. Indexing Options Control Panel: The Indexing Options Control Panel treats Bit. Locker drive states (Off, On, Locked) similar to external drive states (Available, Unavailable). The following table describes the mapping between the Bit.
Locker drive states and the Indexing Control Panel states.
-
Commentaires
